Introduction
Choosing the right type of flash memory can significantly impact the performance, durability, and cost of your storage solution. This article compares SLC (Single-Level Cell), MLC (Multi-Level Cell), TLC (Triple-Level Cell), and QLC (Quad-Level Cell) to help you determine the best option for your needs. it’s essential to understand the differences between SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC. Leading brands such as Samsung, SanDisk, and Kingston offer various options, each with unique advantages. Flash memory is a type of non-volatile storage that retains data even when the power is off, and it’s used in various devices including SSDs, USB drives, and memory cards. Understanding the differences among these types will enable you to make an informed decision for your specific requirements.
What is NAND?
NAND is a type of non-volatile flash memory that retains data even when not connected to a power source. Its ability to preserve data without power makes it an ideal choice for internal, external, and portable devices. USB flash drives, SSDs, and SD cards use flash memory technology to provide storage for devices such as mobile phones or digital cameras.
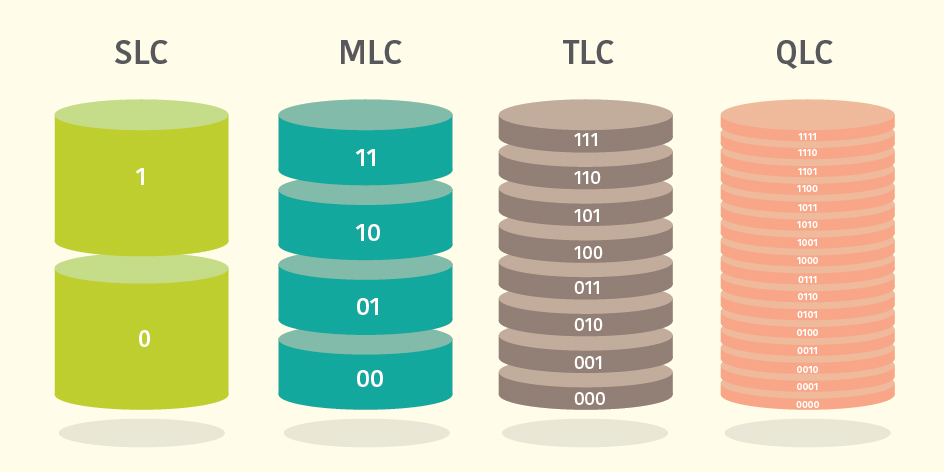
There are several different types of NAND available on the market. The simplest way to classify them is by the number of information bits each storage cell can hold. A bit value is an electrical charge that can be either 0 (off) or 1 (on).
The main differences among various NAND types also include cost, capacity, and durability. Durability is determined by the total number of write/erase cycles (P/E) the flash memory can perform. A write/erase cycle (P/E) refers to the process of writing to and erasing data from a memory cell. The higher the P/E number a NAND technology can handle, the more durable the device will be.
Common types of NAND flash memory include SLC, MLC, TLC, and 3D NAND. This article will discuss the different characteristics of each NAND type.
Understanding Flash Memory Types
Flash memory technology has evolved to meet varying needs, from high-performance enterprise applications to cost-effective consumer electronics. The primary types of flash memory—SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC—differ mainly in the number of bits each cell can store. These differences affect performance, endurance, and cost.
SLC (Single-Level Cell)
- Definition: Stores 1 bit per cell.
- Characteristics: Highest reliability, fastest performance, and greatest endurance.
- Applications: Used in high-performance and critical applications where reliability is paramount.
MLC (Multi-Level Cell)
- Definition: Stores 2 bits per cell.
- Characteristics: Balances performance, capacity, and cost.
- Applications: Common in consumer electronics and enterprise environments where a balance of performance and cost is required.
TLC (Triple-Level Cell)
- Definition: Stores 3 bits per cell.
- Characteristics: Higher capacity and lower cost compared to SLC and MLC, but with reduced performance and endurance.
- Applications: Widely used in consumer electronics such as SSDs, USB drives, and memory cards.
QLC (Quad-Level Cell)
- Definition: Stores 4 bits per cell.
- Characteristics: Maximizes storage density and reduces cost per gigabyte, but has the lowest performance and endurance.
- Applications: Suitable for large-scale data storage where read operations are more frequent than write operations.
Understanding the Role of M.2 Connectors for SSDs
The M.2 connector represents a significant advancement in storage technology, offering new levels of speed and efficiency for SSDs. This innovative connection type can be directly integrated into your motherboard, enabling a streamlined and compact design.
Types of M.2 SSDs:
-
M.2 SATA SSDs:
While sleek and less bulky than traditional methods, these SSDs still utilize the SATA interface. They offer a compact form without sacrificing the reliable, familiar SATA speeds. -
M.2 NVMe SSDs:
This is where the true potential of M.2 shines. By connecting through PCIe lanes, these SSDs leverage the high speeds of PCIe, resulting in significantly faster data transfer rates. This means quicker boot times, faster file transfers, and an overall snappier system performance.
Why M.2 Connectors Matter:
-
Space Efficiency:
The M.2’s compact size frees up valuable space within your computer, allowing for more efficient designs and potentially larger cooling solutions. -
Speed and Performance:
Particularly with NVMe drives, users experience a notable boost in performance, making these drives ideal for gaming, video editing, and other demanding applications. -
Versatility:
The M.2 connector’s ability to support both SATA and PCIe interfaces provides flexibility in choosing storage options based on specific needs and budgets.
Key Differences Among SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC
Understanding the differences among SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC is crucial for selecting the right flash memory type for your needs. These differences primarily revolve around storage capacity, performance, durability, and cost.

How Command Queueing Differs Between SATA and NVMe SSDs
When it comes to command queueing, the differences between SATA and NVMe SSDs are significant and impact performance.
SATA SSDs
- Interface Limitation: SATA drives use the Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI). This was originally designed with hard drives in mind, limiting its efficiency with SSDs.
- Queue Depth: AHCI supports just one command queue, and within that, it can handle 32 pending commands. This is sufficient for rotational hard drives, but it can bottleneck the potential speed of an SSD.
NVMe SSDs
- Designed for Modern Needs: NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is built specifically for SSDs, optimizing the pathway between the storage and the CPU.
- Massive Parallelism: NVMe supports up to 64,000 command queues, and each queue can manage up to 64,000 commands. This allows NVMe SSDs to fully harness the speed of flash technology.
- CPU Efficiency: NVMe’s architecture is less complex and implemented more straightforwardly, which means it draws fewer CPU resources compared to SATA.
Storage Capacity
| Memory Type | Bits Per Cell | Storage Density |
|---|---|---|
| SLC | 1 | Lowest |
| MLC | 2 | Moderate |
| TLC | 3 | High |
| QLC | 4 | Highest |
- SLC: Offers the lowest storage density but excels in performance and reliability.
- MLC: Provides a moderate storage capacity with a good balance of performance and cost.
- TLC: Offers higher storage density, making it cost-effective for consumer electronics.
- QLC: Maximizes storage capacity, making it the most cost-effective option for large-scale data storage
Understanding the Differences: SATA vs. NVMe for SSDs
When choosing between SSDs, you’ll likely encounter the terms SATA and NVMe. These refer to the types of interfaces used, significantly impacting performance and connectivity.
Connection and Speed
SATA (Serial ATA): This is a legacy interface originally developed for HDDs. While SATA SSDs use this same interface, they are limited by its maximum data transfer rate of 600 MB/s. For HDDs, this isn’t an issue since they often cap at under 200 MB/s. However, SATA SSDs can’t reach speeds beyond their ceiling, making them slower compared to their potential.
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express): Leveraging the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) standard, NVMe SSDs boast impressive speeds. Basic models exceed 3,500 MB/s, with PCIe Gen 4 capable of hitting 7,000 MB/s. These speeds allow you to harness extraordinarily fast data processing power.
Functionality Differences
SATA: One notable limitation is its function capability—it can only read or write data at one time, never simultaneously.
NVMe: In contrast, NVMe SSDs are built for multitasking. They allow both reading and writing operations to occur concurrently, enhancing efficiency.
Parallelism and Command Queueing
SATA’s Structure: Utilizing the Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI), it supports a single command queue with up to 32 pending commands.
NVMe’s Robustness: This interface is engineered for parallel processing, supporting up to 64,000 command queues and allowing each queue to manage up to 64,000 commands simultaneously. This capability mimics a multi-core CPU, executing tasks in smaller, faster segments. The result is up to 440,000 random read IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) and 360,000 random write IOPS at a queue depth of 32.
Resource Efficiency
NVMe interfaces require fewer CPU resources due to their streamlined architecture, making them an efficient choice for high-performance computing needs.
Why Bigger Isn’t Always Better for SSD Cells
When it comes to SSDs, one might assume that larger capacity in memory cells is inherently better. However, this isn’t always true due to a few key factors.
Speed Considerations
Writing data to an SSD involves encoding information within its memory cells. Storing more bits in a single cell can slow down this process. Single-Level Cells (SLC) store one bit per cell, allowing for quicker write and read speeds. In contrast, Multi-Level Cells (MLC), Triple-Level Cells (TLC), and Quad-Level Cells (QLC) store multiple bits per cell, which can reduce speed.
Durability and Reliability
Beyond speed, the durability of an SSD is also impacted by how data is stored. Writing and re-writing data to cells gradually wears them out. Since SLC cells handle fewer bits, they undergo less stress and tend to last longer. As more bits are packed into cells with MLC, TLC, or QLC technology, the lifespan of these cells tends to decrease, making them less reliable over time.
Cost-Performance Balance
While SLC SSDs offer superior speed and durability, they come with a hefty price tag. Most consumer SSDs today use technologies like TLC, which balance performance, reliability, and cost. They represent a middle-ground choice, providing adequate speed and lifespan for general use without breaking the bank.
Performance Comparison
Performance is a critical factor when choosing flash memory. SLC provides the best performance, followed by MLC, TLC, and QLC. The number of bits stored per cell directly impacts the read and write speeds.
Read and Write Speeds
| Memory Type | Read Speed | Write Speed |
|---|---|---|
| SLC | Fastest | Fastest |
| MLC | Fast | Fast |
| TLC | Moderate | Moderate |
| QLC | Slowest | Slowest |
- SLC: Offers the highest performance with the fastest read and write speeds, making it ideal for high-performance computing and enterprise applications.
- MLC: Provides a balance of speed and capacity, suitable for general use.
- TLC: While slightly slower, it is cost-effective and widely used in consumer electronics.
- QLC: With high storage density, it is best for large-scale data storage but may not be suitable for performance-critical tasks.
Which NAND SSD is Best for Gaming or Content Creation?
When building a high-performance system, especially for gaming or content creation, choosing the right SSD is crucial. Let’s break down what you need to know about the different types of NAND SSD technologies available.
Types of NAND Technology
-
TLC (Triple-Level Cell):
- Popularity & Performance: TLC is the most widely used type today. It strikes an excellent balance between performance, durability, and cost, making it a favorite among gamers and content creators.
- 3D NAND Advantage: Often paired with 3D NAND technology, TLC SSDs offer improved storage density and reliability.
-
QLC (Quad-Level Cell):
- Cost-Effectiveness: As a newer technology, QLC SSDs are gaining traction due to their lower cost. They store more data per cell, which reduces the cost per gigabyte.
- Drawbacks: While more affordable, QLC drives generally lag in speed and durability compared to TLC options.
Interface Options
- SATA vs. NVMe:
- SATA: Offers decent performance but is limited by older technology speeds.
- NVMe: Provides superior speed and is ideal for those needing rapid data access and retrieval, crucial for gaming and handling large files in content creation.
What to Consider
When choosing between these options, consider the durability metric known as TBW (Terabytes Written). This figure indicates how much data can be written to the drive throughout its lifespan. Compare different models, focusing on those with higher TBW values for better longevity.
Comparing SATA SSDs to NVMe SSDs: A Performance Breakdown
When comparing the performance of SATA SSDs to NVMe SSDs, the difference is substantial, primarily due to their distinct technological frameworks.
Speed and Data Transfer Rates
-
SATA SSDs have a maximum data transfer limit of 600 MB/s. This is generally not an issue for traditional hard drives, which can’t exceed speeds of 200 MB/s. However, for SSDs, this ceiling restricts their potential, leaving them significantly slower compared to their NVMe counterparts.
-
NVMe SSDs boast read speeds that can surpass 3,500 MB/s. With newer PCIe Gen 4 drives, speeds can rocket up to 7,000 MB/s, offering a dramatically faster experience.
Functionality and Capability
-
SATA SSDs are limited to performing either a read or write operation at any given time. This limitation can affect the efficiency of tasks that require simultaneous data reading and writing.
-
In contrast, NVMe SSDs handle multiple tasks concurrently. They can read and write data simultaneously, providing a smoother and quicker performance experience.
Command Queuing and Efficiency
-
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) used by SATA SSDs supports only 32 commands in a single queue. This restricts its ability to handle multiple data processes efficiently.
-
NVMe technology supports up to 64,000 queues, with each queue capable of handling 64,000 commands. This vast capability for parallel processing allows NVMe SSDs to execute complex tasks more swiftly and with fewer CPU resources, thanks to its straightforward design.
Multitasking Proficiency
NVMe SSDs operate similarly to multi-core processors, breaking down lengthy tasks into smaller segments that can be processed simultaneously. This parallel processing powers NVMe drives to achieve up to 440,000 random read IOPS (input/output operations per second) and 360,000 random write IOPS at a standard queue depth of 32.
Performance Impact on Applications
- SLC: Suitable for applications requiring high-speed data access and frequent write operations.
- MLC: Ideal for business and consumer applications that need a balance between performance and cost.
- TLC: Good for everyday use in consumer electronics where moderate performance is acceptable.
- QLC: Best for archival and read-intensive applications where write speed is less critical.
Understanding the Limitations of NVMe SSDs in Consumer PCs
When choosing storage for your consumer PC, it’s essential to recognize the constraints associated with NVMe SSDs compared to their SATA counterparts. Here are the key limitations:
-
PCIe Lane Availability:
- NVMe SSDs rely on PCIe lanes, which are also required by other components like GPUs and network adapters. In typical consumer PCs, the available PCIe lanes range from 16 to 24. With GPUs often taking up to 16 lanes, and network cards occupying a few more, this setup leaves room for only 2 to 3 NVMe SSDs.
-
SATA vs. NVMe Expansion:
- Unlike NVMe SSDs, SATA SSDs don’t compete for PCIe lanes. This difference allows most mid-range to high-end PCs to handle up to 8 SATA SSDs without any contention for those lanes, offering more flexibility for expanding storage.
-
Motherboard Support:
- Motherboards play a crucial role as they determine the number of NVMe slots available, which can be a limiting factor. SATA ports tend to be more plentiful on motherboards, offering greater ease of expansion.
Durability and Longevity
Durability and longevity are essential considerations, especially for applications involving frequent data writing. Flash memory’s endurance is measured by the number of write cycles a cell can withstand before it becomes unreliable.
Endurance and Write Cycles
| Memory Type | Write Cycles | Durability |
|---|---|---|
| SLC | 100,000+ | Highest |
| MLC | 10,000 | High |
| TLC | 3,000-5,000 | Moderate |
| QLC | 1,000 | Lowest |
- SLC: Best endurance with the highest number of write cycles, ideal for critical applications.
- MLC: Good balance of durability and performance, suitable for many business applications.
- TLC: Lower endurance compared to SLC and MLC but more cost-effective for everyday use.
- QLC: Lowest endurance, best suited for read-intensive applications.
Understanding TBW (Total Terabytes Written) and Its Importance for SSD Durability
When exploring the world of Solid State Drives (SSDs), you’ll often come across the term TBW, or Total Terabytes Written. But what does this mean exactly, and why is it crucial for the durability of your SSD?
Defining TBW
TBW represents the total amount of data that an SSD can write over its lifetime before it’s expected to start failing. This value is a key indicator of the drive’s endurance, telling us how much reading and writing can occur before the memory cells wear out.
Why TBW Matters
-
Durability Indicator: TBW is a direct measure of the drive’s durability. It tells users how much data they can write without worrying about the drive failing prematurely.
-
Longevity Assurance: An SSD with a higher TBW value can handle more data transfers over its life, making it a better choice for users with heavy write-intensive needs, like video editing or database management.
-
Maintenance Planning: Knowing the TBW rating helps in planning drive replacements and backups, ensuring data integrity over time.
Implications for Usability
While SSDs have a finite lifespan, most users will find that even moderate TBW ratings suffice for several years of regular use. However, for power users who frequently write large amounts of data, a higher TBW is an important consideration to avoid unexpected drive failure.
In summary, understanding TBW equips you with the knowledge to choose the right SSD for your needs, ensuring that your data storage is both reliable and long-lasting.
Usage Considerations
- SLC: Ideal for data centers, enterprise storage, and industrial use where high durability is required.
- MLC: Suitable for most business and consumer applications.
- TLC: Adequate for general use in consumer electronics and everyday applications.
- QLC: Best for applications where data is mostly read, such as media streaming or data archiving.
Cost Analysis
Cost is a significant factor in choosing flash memory. The cost per gigabyte decreases as the number of bits per cell increases, making QLC the most cost-effective option for large storage needs.
Cost Per Gigabyte
| Memory Type | Cost Per GB | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|
| SLC | Highest | Critical applications |
| MLC | High | General business and consumer |
| TLC | Moderate | Consumer electronics |
| QLC | Lowest | Large-scale storage, budget |
- SLC: While offering the best performance and durability, it is the most expensive.
- MLC: More affordable with good performance and durability.
- TLC: Further reduction in cost, suitable for general use.
- QLC: Most cost-effective in terms of storage capacity, ideal for budget-conscious applications requiring large storage volumes.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- SLC: Best for applications where performance and reliability are crucial despite higher costs.
- MLC: Good for businesses needing reliable performance at a lower cost than SLC.
- TLC: Suitable for consumers looking for a balance of cost and performance.
- QLC: Ideal for large data storage needs where cost savings are paramount.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Flash Memory Type
Each type of flash memory has its strengths and ideal use cases. Understanding these can help you choose the best memory type for your specific needs.
SLC: Critical Applications
- Data Centers: High reliability and performance are critical for server operations.
- Enterprise Storage: Ensures data integrity and speed for business-critical applications.
- High-Performance Computing: Ideal for applications requiring fast and reliable data access.
- Industrial Use: Durable and reliable for harsh environments and critical systems.
MLC: General Business and Consumer Applications
- Laptops and Desktops: Balanced performance and cost make it suitable for everyday computing.
- Digital Cameras: Reliable performance for storing high-quality images and videos.
- Smartphones and Tablets: Good balance of storage capacity and performance for mobile devices.
- Enterprise Applications: Suitable for business environments requiring reliable data storage.
TLC: Consumer Electronics and General Storage
- SSDs for Laptops and Desktops: Cost-effective storage for general computing needs.
- USB Drives: Portable storage with adequate performance for everyday use.
- Memory Cards: Used in cameras, phones, and other consumer electronics for data storage.
- Home Media Centers: Suitable for storing and accessing large media files.
QLC: Large-Scale Storage and Budget Solutions
- Data Archiving: Cost-effective solution for storing large volumes of data.
- Media Libraries: Ideal for applications where data is read more often than written.
- Read-Intensive Applications: Suitable for applications that require high storage capacity at a low cost.
- Budget Storage Solutions: Best for users who need large storage volumes without a significant investment in performance.
Future Trends in Flash Memory Technology
Advancements in flash memory technology are continually pushing the boundaries of performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Several trends are shaping the future of flash memory:
3D NAND Technology
3D NAND technology stacks memory cells vertically to increase storage density and performance. This technology allows for more data to be stored in a smaller physical space, leading to higher capacities and improved efficiency.
New Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Innovations in materials and manufacturing processes are enhancing the durability and reducing the costs of flash memory. These advancements lead to better performance and longer-lasting memory cells.
Enhanced Security Features
As data security becomes increasingly important, future flash memory technologies are expected to include advanced security features such as hardware-based encryption and biometric access controls. These features will help protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Flash memory is being integrated with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and edge computing. These integrations enhance the capabilities of flash memory, making it more versatile and powerful for a wide range of applications.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Choosing the right flash memory depends on your specific needs. Each type of flash memory—SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC—offers distinct advantages and trade-offs in terms of performance, durability, and cost.
- SLC: Ideal for high-performance and high-durability applications.
- MLC: Balanced option for most business and consumer uses.
- TLC: Cost-effective for general use.
- QLC: Best for high-capacity, budget-conscious storage needs.
By understanding the differences and ideal use cases for each type, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your performance requirements and budget constraints.
Explore Our Flash Memory Products
Discover our range of high-quality flash memory products tailored to meet your business needs. Visit our product page to find the perfect solution for your storage requirements.