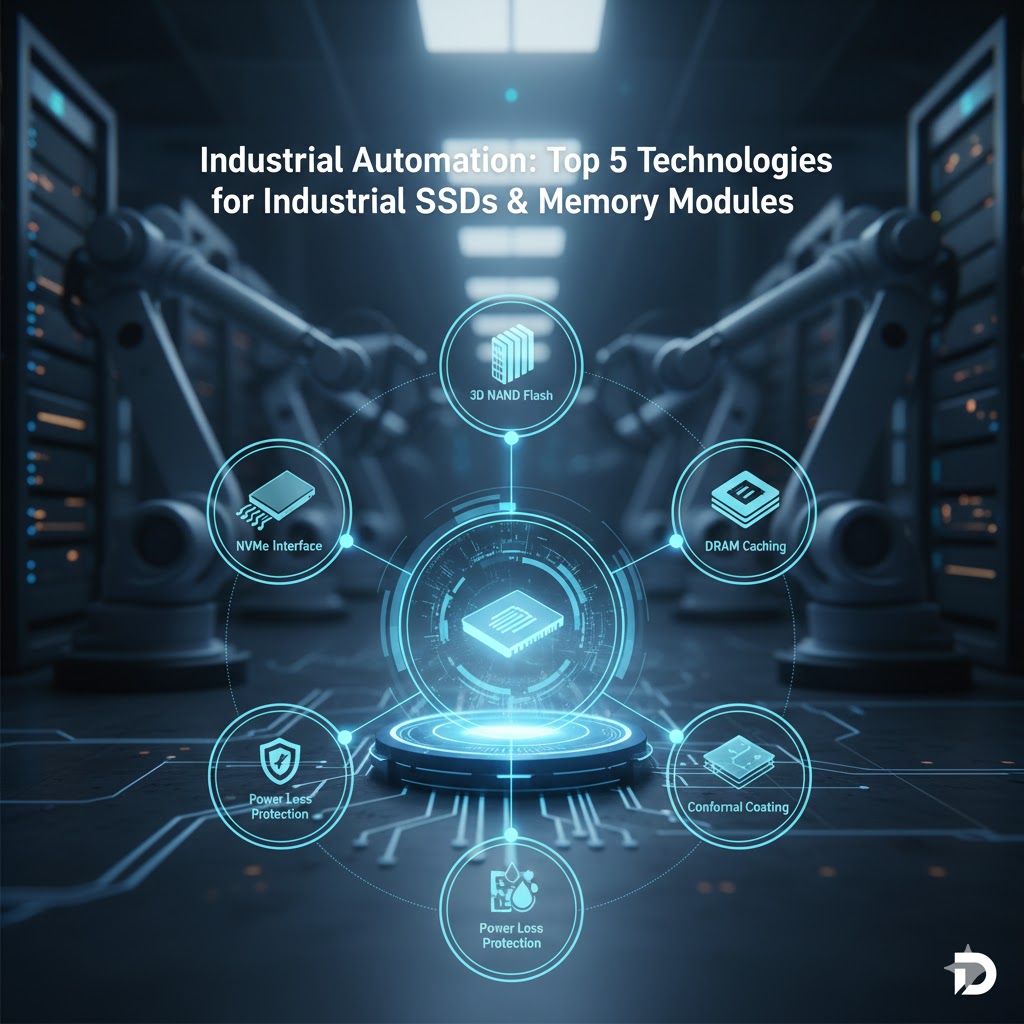
Comprehensive Analysis of Storage Solutions for the Industrial and Automation Sector
Industrial SSD solutions are essential for Industrial Automation systems, as the reliability of highly resilient storage is absolutely critical for ensuring seamless operations, data integrity, and system resilience. As industries increasingly adopt advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) data center ecosystems and IoT integration, the demand for robust, high-performance storage devices has surged. The backbone of these advanced systems lies in specialized storage components designed to withstand the unique rigors of factory floors and remote operating sites.
Overview of Industrial SSDs and Memory Modules
Solid State Drives (SSDs) and memory modules are core components that facilitate data storage and retrieval within these demanding environments. SSDs are non-volatile storage devices that utilize NAND flash memory to persistently store data, offering superior features such as faster access times and higher durability compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs).
Memory modules, including DRAM and embedded memory solutions, serve different yet complementary roles:
-
DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory): Acts as volatile storage, providing quick data access essential for processing tasks and real-time computation.
-
Embedded Memory (e.g., eMMC, BGA SSD): Serves as semi-permanent, compact storage, enabling data access and system boot functions in space-constrained embedded controllers.
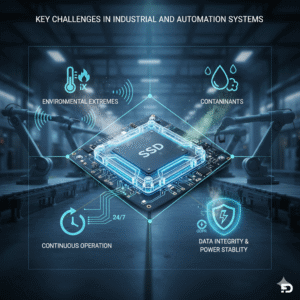
Key Challenges in Industrial and Automation Systems
The operating environments of industrial automation systems present distinct challenges that consumer-grade storage cannot meet. These challenges necessitate the use of specialized Industrial SSDs:
-
Environmental Extremes: Exposure to shock, vibration, and extreme temperatures. Maintaining data integrity and system performance under these conditions requires specialized storage solutions.
-
Contaminants: Presence of dust, moisture, and corrosive elements.
-
Continuous Operation: The need for 24/7 reliability, where downtime can lead to significant financial losses.
-
Data Integrity: Maintaining data integrity under unstable power conditions and meeting strict data protection regulations like GDPR.
Additionally, adherence to standards such as conformal coating for hardware protection are critical considerations.
Critical Role and Advanced Technologies of Industrial SSDs
Industrial SSDs play a critical role in enhancing the reliability and performance of industrial automation systems. Their design is inherently focused on endurance and data protection beyond mere speed.
Enhancing Reliability with Specialized Features
Ruggedized Industrial SSDs are engineered to ensure high availability and durability, thereby reducing maintenance needs and preventing costly data loss. Key reliability features include:
-
Power Loss Protection (PLP): This hardware and firmware-based mechanism uses capacitors to supply temporary power to the SSD controller in the event of an unexpected power failure. This crucial time allows the controller to complete all data writes in its volatile cache and flush mapping tables to the NAND, ensuring data integrity.
-
Wide-Temperature Operation: The ability to function consistently across extreme temperature ranges is paramount for outdoor or non-climate-controlled industrial settings.
-
Conformal Coating: A protective chemical layer applied to the PCB to shield components from moisture, dust, and corrosive elements, ensuring longevity in harsh environments like oil and gas exploration sites.
NAND Flash Technology and Endurance
The choice of NAND Flash memory is fundamental to the endurance of an Industrial SSD. Endurance is typically measured by TBW (Total Bytes Written) or DWPD (Drive Writes Per Day):
| NAND Type | Endurance (P/E Cycles) | Application Suitability |
| SLC (Single-Level Cell) | Highest (Approx. 60K-100K) | Highly mission-critical, continuous write/heavy data logging. |
| MLC (Multi-Level Cell) | Medium (Approx. 3K) | Balancing cost and endurance; suitable for mixed workloads. |
| TLC (Triple-Level Cell) | Lowest (Approx. 500-1K) | Cost-sensitive, read-intensive applications. |
| pSLC (Pseudo SLC) | Enhanced MLC/TLC (Up to 20K) | Industrial Automation standard. It configures MLC/TLC to store only one bit per cell, significantly boosting endurance while maintaining better cost-effectiveness than true SLC. |
The utilization of pSLC technology in Industrial SSDs is a major differentiator, offering robust endurance critical for applications with continuous data logging and monitoring. Industrial-grade NAND Flash Memory and DRAM Modules are manufactured to meet rigorous standards, offering enhanced endurance, reliability, and data retention.
Boosting Performance with NVMe and Advanced Interfaces
High-speed interfaces such as NVMe and PCIe enable rapid data transfer, facilitating the real-time processing essential for modern industrial automation control, AI data center ecosystems, and advanced analytics.
-
NVMe/PCIe: These interfaces ensure minimal latency and maximum throughput, which is essential for AI data center ecosystems and high-frequency trading environments.
-
Advanced Firmware: Industrial-grade firmware includes proprietary wear-leveling algorithms, advanced error correction codes (ECC/LDPC), and bad block management, ensuring optimal drive longevity and data integrity throughout the device’s lifespan.
-
Security Features: Enhanced security measures, including AES key length options and secure firmware updates, help meet data protection regulation requirements and prevent unauthorized access.
Application Scenarios and Best Practices in Industrial Automation
The appropriate selection and deployment of storage solutions are crucial for maximizing performance and reliability across various sectors within industrial automation.
Key Industrial Automation Applications
-
Industrial PCs (IPCs) and Manufacturing Control Systems: These systems utilize ruggedized SSDs and high-capacity memory modules to ensure continuous operation, data logging, and real-time control. They require compliance with standards such as CE, UL, and conformal coating requirements.
-
Railway, Transportation, and Traffic Management: This sector deploys durable Industrial SSDs with vibration and temperature resistance to support critical infrastructure. Redundancy strategies, such as RAID configurations and data backup protocols, are vital for system resilience.
-
Smart Factories and IoT Integration: This involves implementing high-speed NVMe SSDs and cache hard disks to handle massive data flows. Adopting best practices like account contact management and accounts create procedures can streamline device provisioning and maintenance.
-
Energy Management Systems (e.g., Power Plants): These systems leverage embedded storage solutions for compactness and reliability. They must follow data protection regulation GDPR guidelines and incorporate secure data encryption to safeguard sensitive operational data.
-
Oil and Gas Exploration and Processing: This requires industrial-grade NAND flash and DRAM modules capable of withstanding harsh environments. It is recommended to regularly accept privacy policy updates and ensure compliance with data security standards.
Deployment and Selection Best Practices
Engineers selecting Industrial SSDs for industrial automation projects must evaluate the following criteria:
-
Durability: Prioritize shock, vibration, and temperature resistance.
-
Capacity: Match storage size to operational data requirements.
-
Interface Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing hardware interfaces like PCIe, SATA, or NVMe.
-
Compliance Standards: Verify adherence to data protection regulation GDPR and industry-specific certifications.
-
Installation and Maintenance: Follow manufacturer guidelines, including conformal coating application and regular firmware updates.
-
Data Backup and Redundancy: Implement disaster recovery strategies, including off-site backups and redundant storage configurations.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
This comprehensive analysis underscores the vital role of specialized Industrial SSDs and memory modules in enhancing the reliability, security, and performance of industrial automation systems. Strategic selection based on environmental resilience, interface compatibility, and critical features like PLP and pSLC technology is essential for optimizing infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is Power Loss Protection (PLP) so critical for Industrial Automation applications?
PLP is vital for industrial settings because unexpected power failures can lead to data loss or corruption. PLP uses hardware capacitors to supply temporary power to the SSD controller, allowing it to complete all data writes in its cache and flush mapping tables to the NAND flash. This mechanism ensures data integrity and enhances overall system resilience.
Q2: How do NVMe and SATA interfaces compare for Industrial SSD selection?
NVMe over PCIe offers significantly higher throughput and lower latency compared to the legacy SATA interface. NVMe is ideal for high-speed data transfer required by AI data center ecosystems and edge computing. SATA, while slower, is suitable for traditional Industrial PCs (IPCs) and smaller embedded systems, often offering better backward compatibility.
Q3: How does pSLC technology enhance the endurance and lifespan of an Industrial SSD?
pSLC (Pseudo SLC) is a firmware technique that configures lower-cost MLC/TLC NAND to store only a single bit per cell, mimicking true SLC. This dramatically increases the number of program/erase cycles (P/E cycles), boosting endurance up to 20,000 P/E cycles. This makes pSLC a cost-effective, high-endurance choice for heavy-write workloads in Industrial Automation.
Q4: What are the primary environmental compliance factors when deploying Industrial SSDs?
Key factors include resistance to shock, vibration, and temperature extremes. Additionally, compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and adherence to hardware protection standards, such as conformal coating to guard against moisture and corrosive elements, are essential for longevity and data security.
Q5: For Smart Factories, what are the best practices for managing Industrial SSDs?
Smart Factories should implement high-speed NVMe SSDs to handle massive data flows from IoT devices. Best practices include following manufacturer guidelines for regular firmware updates and deploying redundancy strategies like RAID configurations to enhance system resilience and prevent data loss.
Looking ahead, advancements such as energy-efficient storage options, highly integrated security features, and innovations driven by AI data center ecosystems will continue to shape the future of industrial storage solutions. By staying informed about emerging technologies, adhering to data protection regulation GDPR, and considering practical deployment strategies like conformal coating and form factor selection, engineers can ensure their systems are resilient, scalable, and prepared for future technological advancements, including advances in artificial intelligence and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Contact Dellwa today to protect your industrial operations with certified industrial SSDs.